创建基本的wxPython程序
主题:
- 创建一个基本的wxPython程序
- 将这个程序打造成一个简单的文本编辑器
本节将介绍如何使用wxPython构建一个小型的文本编辑器。通过这个看似复杂的任务你将会体验到wxPython有多方便和简单。
概述
每当大家提前GUI编程的时候,总是会牵扯到窗体,菜单,鼠标,图标等等。或许你的第一感觉wx.Windows就对应一个显示在屏幕上的窗口,但你错了,在wxPython中,wx.Window表示任意可以显示在屏幕上的东西的对象,wx.Window这个类是所有屏幕上可见的对象的基类,诸如输入框,下拉列表都是由它派生而来。屏幕上的可见对象都有一些共同的属性和行为,比如位置,尺寸,是否可见,是否处于输入焦点等等,这些在wx.Window里面都有定义。 所以如果你要找一个类来表示窗口,就应该用继承自wx.Window的wx.Frame而不是wx.Window. wx.Frame实现了所有与屏幕相关的行为和属性(当然如果wx.Frame位于MDI中则另当别论) .要创建一个窗体,可以用wx.Frame,也可以用其子类如wx.Dialog,但不能再按照思维定势去想wx.Window了。
一个简单的例子
添加编辑控件
要编写一个文本编辑器,首先当然需要一个编辑控件,如下:import wx class MainWindow(wx.Frame): """ We simply derive a new class of Frame. """ def __init__(self, parent, id, title): wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id, title, size=(200,100)) self.control = wx.TextCtrl(self, 1, style=wx.TE_MULTILINE) self.Show(True) app = wx.PySimpleApp() frame=MainWindow(None, wx.ID_ANY, 'Small editor') app.MainLoop()
(需要注意的是这里我们定义了一个继承自wx.Frame的类,在类的初始化方法最后调用了父类的show方法,这也就不需要在额外调用show方法。) 如你所见,这段代码还是非常简洁, 我们所做的只是继承了一个wxFrame然后覆写了它的构造函数,在构造函数中新建一个简单的文本编辑框控件,就这样,就有了如下的效果图:
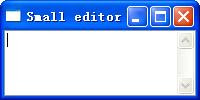
添加菜单栏
多数你所见到的GUI程序都有一个菜单栏和一个状态栏,下面就开始添加这两个组件:import wx ID_ABOUT=101 ID_EXIT=110 class MainWindow(wx.Frame): def __init__(self,parent,id,title): wx.Frame.__init__(self,parent,wx.ID_ANY, title, size = (300,200)) self.control = wx.TextCtrl(self, 1, style=wx.TE_MULTILINE) self.CreateStatusBar() # A Statusbar in the bottom of the window # Setting up the menu. filemenu= wx.Menu() filemenu.Append(ID_ABOUT, "&About"," Information about this program") filemenu.AppendSeparator() filemenu.Append(ID_EXIT,"E&xit"," Terminate the program") # Creating the menubar. menuBar = wx.MenuBar() menuBar.Append(filemenu,"&File") # Adding the "filemenu" to the MenuBar self.SetMenuBar(menuBar) # Adding the MenuBar to the Frame content. self.Show(True) app = wx.PySimpleApp() frame = MainWindow(None, -1, "Sample editor") app.MainLoop()
- 菜单有了,但是点击菜单却没有任何反应,下面添加事件处理:
实战事件处理
- 对事件做处理就是人们常说的事件处理,wxPython的一大特色就是在事件处理上有极高的灵活性。接下来我们将添加一下实战的代码,这些代码或许已经超越了基于前面一章的理解能力,所以对他们的讨论将放到后续章节。 简单的说,一个事件就是一条发送到wxPython得消息告知有什么事情发生了,需要处理了 [6].通常来说,你所要做的就是把这个事件连接到一个特定的方法,让这个方法去处理,仅仅需要调用
EVT_*. (Also see Avoiding EVT_MENU.) 方法,如下:
EVT_MENU(self, ID_ABOUT, self.OnAbout)
这个函数的作用在将对菜单ID 为ID_ABOUT的事件都扔给self.OnAbout去处理。self.OnAbout函数可能就像下面这个样子:
def OnAbout(self, event)
OnAbout的参数是event对象,它所做的就是在事件发生时: - 跳过这个事件, 让事件在事件处理周期里转到另外的处理程序。
或者处理这个事件,事件消息在被程序处理后就不会在事件处理周期继续传播。
让我们看看现在的程序:
import os
import wx
ID_ABOUT=101
ID_EXIT=110
class MainWindow(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self,parent,id,title):
wx.Frame.__init__(self,parent,wx.ID_ANY, title, size = (200,100))
self.control = wx.TextCtrl(self, 1, style=wx.TE_MULTILINE)
self.CreateStatusBar() # A StatusBar in the bottom of the window
# Setting up the menu.
filemenu= wx.Menu()
filemenu.Append(ID_ABOUT, "&About"," Information about this program")
filemenu.AppendSeparator()
filemenu.Append(ID_EXIT,"E&xit"," Terminate the program")
# Creating the menubar.
menuBar = wx.MenuBar()
menuBar.Append(filemenu,"&File") # Adding the "filemenu" to the MenuBar
self.SetMenuBar(menuBar) # Adding the MenuBar to the Frame content.
wx.EVT_MENU(self, ID_ABOUT, self.OnAbout) # attach the menu-event ID_ABOUT to the
# method self.OnAbout
wx.EVT_MENU(self, ID_EXIT, self.OnExit) # attach the menu-event ID_EXIT to the
# method self.OnExit
self.Show(True)
def OnAbout(self,e):
d= wx.MessageDialog( self, " A sample editor \n"
" in wxPython","About Sample Editor", wx.OK)
# Create a message dialog box
d.ShowModal() # Shows it
d.Destroy() # finally destroy it when finished.
def OnExit(self,e):
self.Close(True) # Close the frame.
app = wx.PySimpleApp()
frame = MainWindow(None, -1, "Sample editor")
app.MainLoop()
更多有趣的东西
- 如果一个文本编辑器不能保存用户的输入,不能打开一个已有的文档,那这个编辑器可以算一个废品。下面我们加上打开已有文档的代码,通过一个系统的文件浏览对话框打开文件:
def OnOpen(self,e): """ Open a file""" self.dirname = '' dlg = wx.FileDialog(self, "Choose a file", self.dirname, "", "*.*", wx.OPEN) if dlg.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK: self.filename=dlg.GetFilename() self.dirname=dlg.GetDirectory() f=open(os.path.join(self.dirname,self.filename),'r') self.control.SetValue(f.read()) f.close() dlg.Destroy()- 上面的代码其实只有简单的三个步骤:
- 首先,创建一个系统的文件浏览对话框
然后,调用ShowModal方法,弹出一个模态对话框,等待用户按下OK按钮或者Cancel按钮。
- 最后,得到用户所选择的文件夹和文件名,调用destroy方法然后销毁这个窗口
可能的扩展
我们的编辑器还远远不能算是一个专业的编辑器,还有更多的技术可以用到这个编辑器上让它更专业,诸如:- 拖拽操作.
- MDI (多窗口窗体)
- Tab view/multiple files (通过标签视图显示更多文件)
- Find/Replace dialog (查找,替换功能)
Print dialog (打印功能)
- Macro-commands in python ( 在编辑器里面编写Python代码并运行)
- etc ...
- 上面的代码其实只有简单的三个步骤:

 代码很短很强大,首先导入wx 模块,然后初始化一个wx.PySimpleApp对象,接下来是窗口对象wx.Frame,一个有标题栏,最小最大关闭按钮的窗口就创建好了[4],调用show方法让这个窗口显示出来。最后一句MainLoop作用则是使整个程序进入事件循环,学过Swing的可能会觉得这句话似乎有点多余,个人感觉可能是由于与平台底层GUI控件的兼容,诸如MFC之类的GUI的事件其实就是一个无限循环,无限的去循环检查有没有新的事件产生,并调用相应的处理函数。回到wx.Frame创建这里,这应该是这几句Code中看起来稍微复杂的一句了:
代码很短很强大,首先导入wx 模块,然后初始化一个wx.PySimpleApp对象,接下来是窗口对象wx.Frame,一个有标题栏,最小最大关闭按钮的窗口就创建好了[4],调用show方法让这个窗口显示出来。最后一句MainLoop作用则是使整个程序进入事件循环,学过Swing的可能会觉得这句话似乎有点多余,个人感觉可能是由于与平台底层GUI控件的兼容,诸如MFC之类的GUI的事件其实就是一个无限循环,无限的去循环检查有没有新的事件产生,并调用相应的处理函数。回到wx.Frame创建这里,这应该是这几句Code中看起来稍微复杂的一句了:



